Colour tv ( CRT/ LCD/ LED ) Repairing, Colour tv service code, Circuit Diagram, Basic Electronics, Shematics Project ( Arduino, Simple Electronics, Robotics, 555 IC ), DTH Tricks Cable TV Solution, IC Data Sheet And Many More.
Sunday 31 March 2019
Engineer Spotlight: Tony Armstrong of Analog Devices
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2FGUNbm
Friday 29 March 2019
ROHM Announces New Automotive-Grade SIC MOSFET Series
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2YJ53Zo
Introduction to Reliability in Electronics: Tools and Metrics for Anticipating Device Failure
from All About Circuits Technical Articles https://ift.tt/2CHhdZc
Loop-Based Anti-Theft Alarm
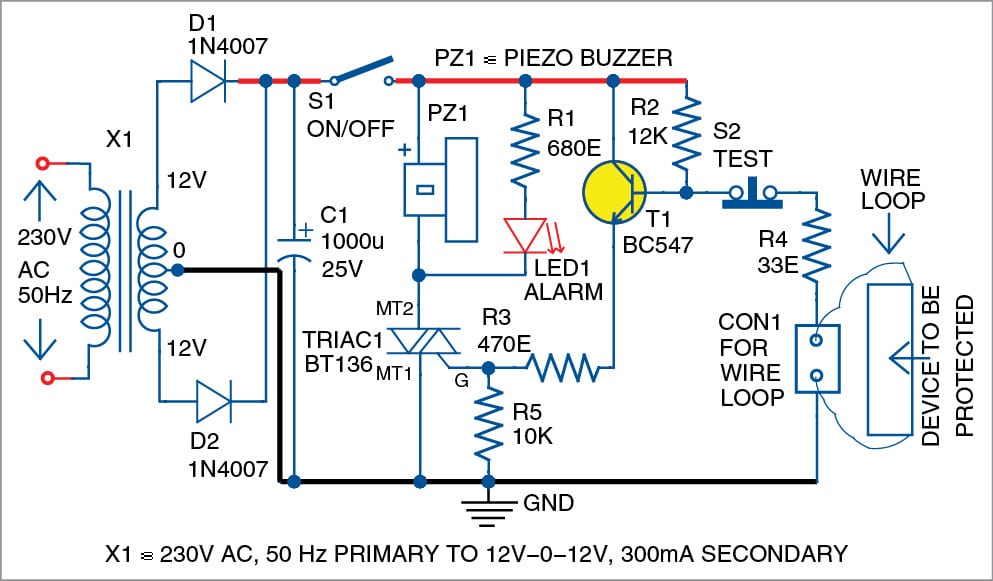 Presented here is a triac-based anti-theft alarm circuit using a simple wire loop as sensor. It can be used to protect any device against theft, or as a door opening alarm. Make sure that when the device moves, or the door opens, the sensing loop breaks, too. The author’s prototype is shown in Fig. 1. […]
Presented here is a triac-based anti-theft alarm circuit using a simple wire loop as sensor. It can be used to protect any device against theft, or as a door opening alarm. Make sure that when the device moves, or the door opens, the sensing loop breaks, too. The author’s prototype is shown in Fig. 1. […]
The post Loop-Based Anti-Theft Alarm appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2JOEoH8
Murata Features Low-Power, High Efficiency With New Components
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2FJhcGc
Thursday 28 March 2019
How to Choose the Right Microcontroller for Your Application
from All About Circuits Technical Articles https://ift.tt/2TZTMVE
UnitedSiC Announces SiC JFET Family for Low Power AC-DC Flyback Converters
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2Wrc3bb
SENSORS: How To Check Food Adulteration
 Nowadays, adulteration is being done in sophisticated ways that demand cutting-edge research for the detection of adulterants. Due to changing social values where companies are focussing on reaping rich profits, adulteration is prevalent in almost all commodities such as food items, fuel, cloths and construction materials. Adulteration has reached alarming levels and is, hence, making […]
Nowadays, adulteration is being done in sophisticated ways that demand cutting-edge research for the detection of adulterants. Due to changing social values where companies are focussing on reaping rich profits, adulteration is prevalent in almost all commodities such as food items, fuel, cloths and construction materials. Adulteration has reached alarming levels and is, hence, making […]
The post SENSORS: How To Check Food Adulteration appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2YvUCbl
Wednesday 27 March 2019
Popular Toshiba Flash Memory Platform Now Qualified for Automotive Applications
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2UUSPue
New Renesas Power Modules Claim Highest Density at 10A and 15A, Leverage New Packaging and PMBus
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2YuNpID
Half & Full Wave Rectifier | Rectifier Basics
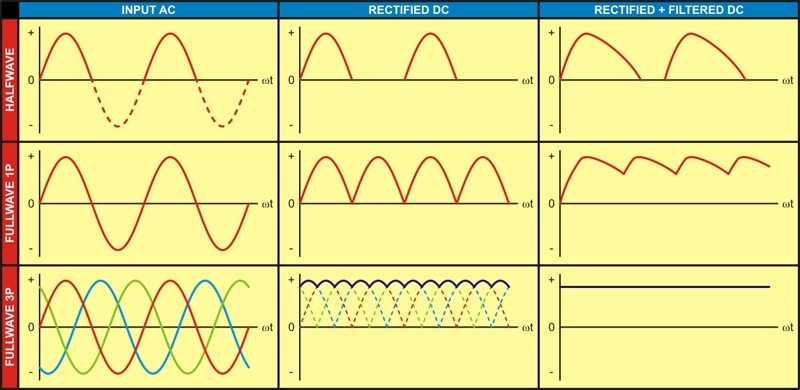 Power conversion is very common with today’s electronics. We constantly switch from AC to DC and vice-versa. The common source of AC is the power supply whereas, batteries are used for DC power as and when required. The conversion from AC to DC is, however, an easier way instead of buying a new battery every […]
Power conversion is very common with today’s electronics. We constantly switch from AC to DC and vice-versa. The common source of AC is the power supply whereas, batteries are used for DC power as and when required. The conversion from AC to DC is, however, an easier way instead of buying a new battery every […]
The post Half & Full Wave Rectifier | Rectifier Basics appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2V4k5qt
Capacitive Reactance
 A capacitor by structure consists of two conductors separated by an insulator that is often referred to as a dielectric. It is often used to filter out DC component in electronics circuits as it only allows DC component to pass through. Meaning, for very low frequencies (high DC component low AC component), the capacitor acts […]
A capacitor by structure consists of two conductors separated by an insulator that is often referred to as a dielectric. It is often used to filter out DC component in electronics circuits as it only allows DC component to pass through. Meaning, for very low frequencies (high DC component low AC component), the capacitor acts […]
The post Capacitive Reactance appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2U0R7uP
Tuesday 26 March 2019
Innovative Isolated ICs from Silicon Labs Promise Precision and Stability
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2uwcw02
Automatic Infrared Faucet Controller
 Described here is an easy-to-use circuit of an automatic infrared (IR) faucet controller suitable for hand hygiene and water conservation at homes, hospitals and offices. With this compact controller you can turn on and off a faucet automatically, preventing water wastage and saving energy costs. The core part of the faucet controller is an electronic […]
Described here is an easy-to-use circuit of an automatic infrared (IR) faucet controller suitable for hand hygiene and water conservation at homes, hospitals and offices. With this compact controller you can turn on and off a faucet automatically, preventing water wastage and saving energy costs. The core part of the faucet controller is an electronic […]
The post Automatic Infrared Faucet Controller appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2UYgnyy
Monday 25 March 2019
What Is a Microcontroller? The Defining Characteristics and Architecture of a Common Component
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2FqrVUy
TDK Claims World’s Smallest Point-of-Load DC-DC Converter
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2OmY2se
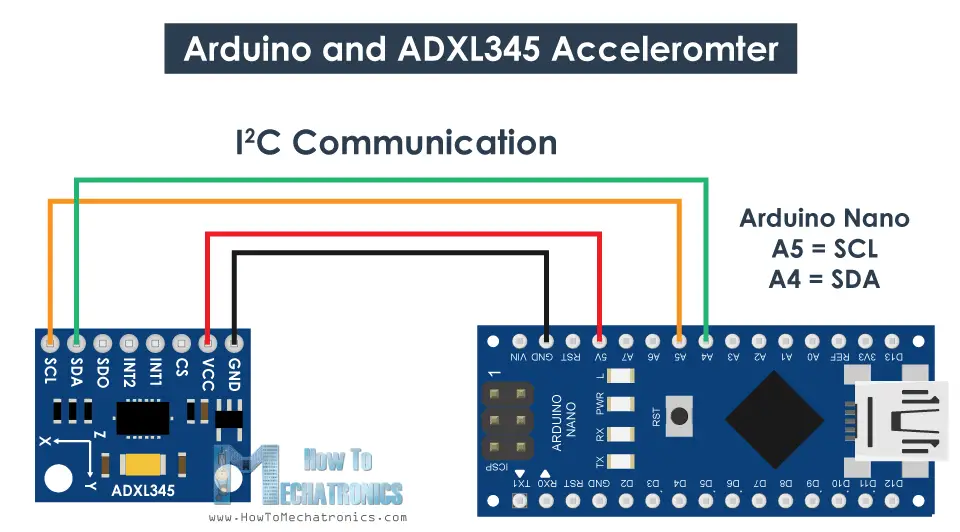
How To Track Orientation with Arduino and ADXL345 Accelerometer
In this tutorial we will learn how to measure angle and track orientation using the Arduino and the ADXL345 Accelerometer sensor. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below for more details.
First, I will explain how the sensor work and how to read the data from it, and then using the Processing development environment, we will make a 3D visualization of the accelerometer orientation.
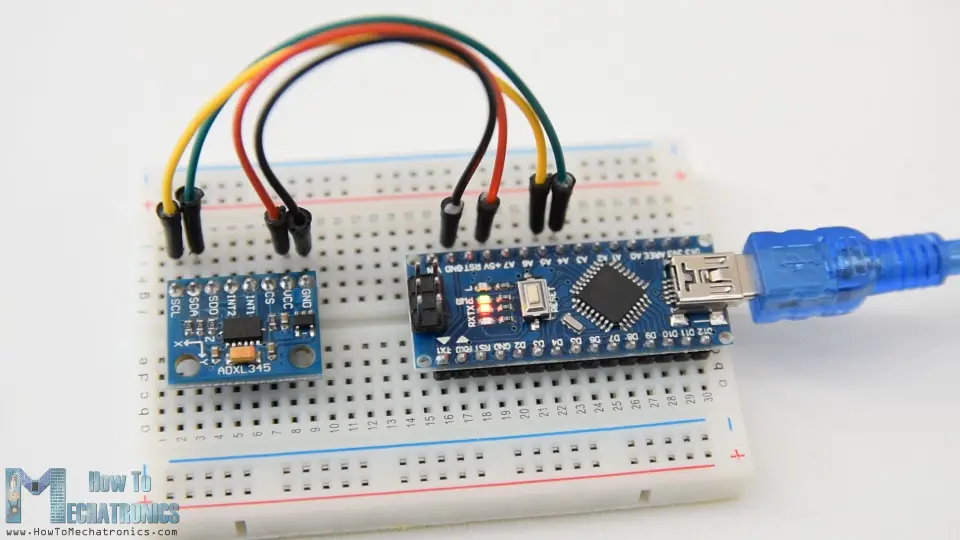
How ADXL345 Accelerometer Works
To begin with, let’s take a look how the ADXL345 sensor works. This is a 3-axis accelerometer which can measure both static and dynamic forces of acceleration. The earth gravitational force is a typical example of static force, while dynamic forces can be caused by vibrations, movements and so on.
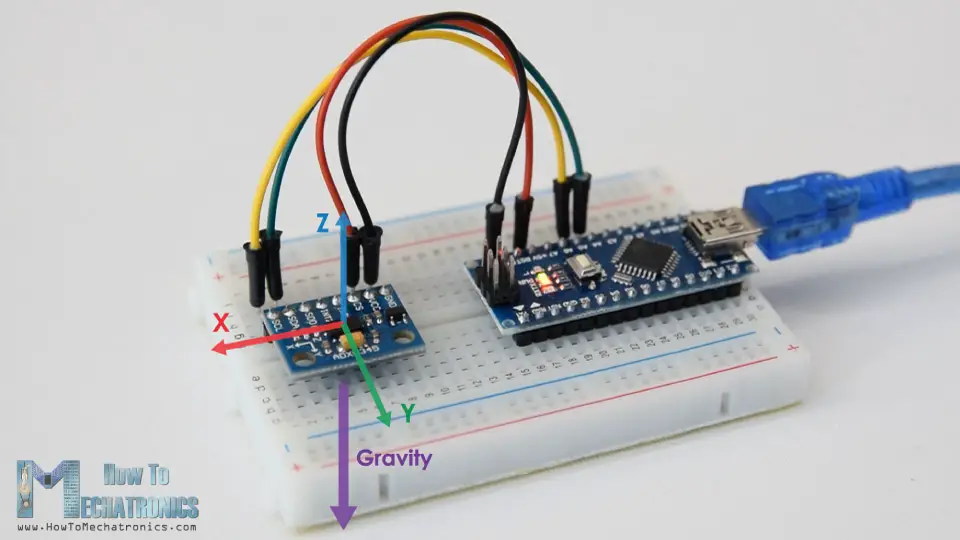
The unit of measurement for acceleration is meter per second squared (m/s^2). However, accelerometer sensors usually express the measurements in “g” or gravity. One “g” is the value of the earth gravitational force which is equal to 9.8 meters per second squared.
So, if we have an accelerometer positioned flat, with its Z-axis pointing upwards, opposite to the gravitational force, the Z-axis output of the sensor will be 1g. On the other hand, the X and Y outputs will be zero, because the gravitational force is perpendicular to these axes and doesn’t affect them at all.
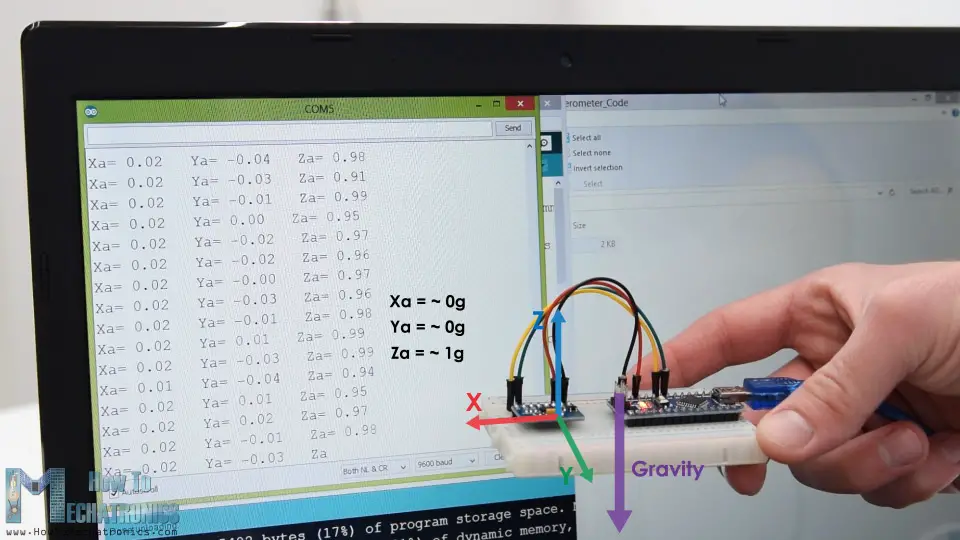
If we flip the sensor upside down, then the Z-axis output will be -1 g. This means that the outputs of the sensor due to its orientation to gravity can vary from -1g to +1g.
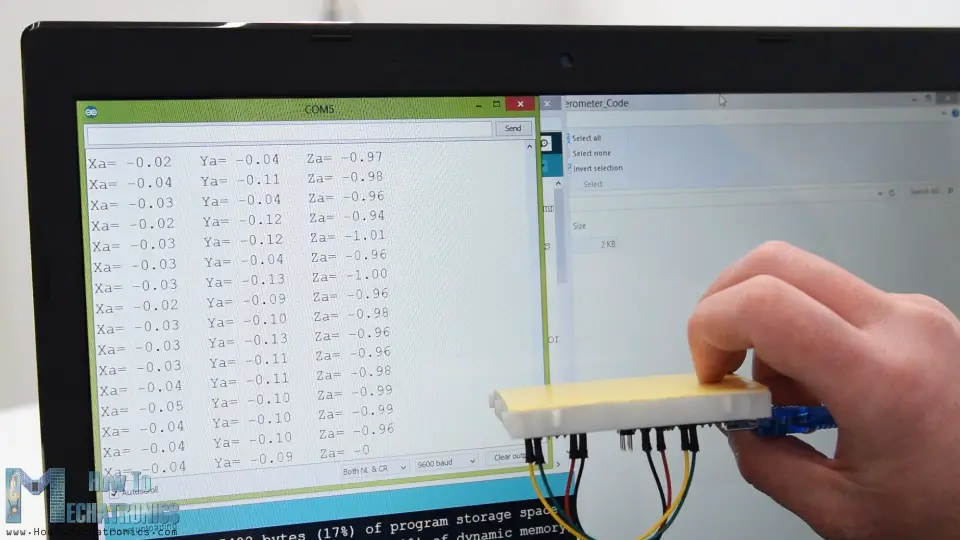
So according to this data and using some trigonometry math, we can calculate the angle at which the sensor is positioned.
How to Read ADXL345 Accelerometer Data with Arduino
Ok, now let’s see how we can read the ADXL345 accelerometer data using the Arduino. This sensor uses the I2C protocol for communication with the Arduino so we need only two wires for connecting it, plus the two wires for powering it.
You can get the components needed for this Arduino Tutorial from the links below:
- ADXL345 Accelerometer ………………. Amazon / Banggood
- Arduino Board …………………………….. Amazon / Banggood
- Breadboard and Jump Wires ………… Amazon / Banggood
*Please note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
ADXL345 Accelerometer Arduino Code
Here’s the Arduino code fo reading the ADXL345 accelerometer data.
/*
Arduino and ADXL345 Accelerometer Tutorial
by Dejan, https://howtomechatronics.com
*/
#include <Wire.h> // Wire library - used for I2C communication
int ADXL345 = 0x53; // The ADXL345 sensor I2C address
float X_out, Y_out, Z_out; // Outputs
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initiate serial communication for printing the results on the Serial monitor
Wire.begin(); // Initiate the Wire library
// Set ADXL345 in measuring mode
Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345); // Start communicating with the device
Wire.write(0x2D); // Access/ talk to POWER_CTL Register - 0x2D
// Enable measurement
Wire.write(8); // (8dec -> 0000 1000 binary) Bit D3 High for measuring enable
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(10);
}
void loop() {
// === Read acceleromter data === //
Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345);
Wire.write(0x32); // Start with register 0x32 (ACCEL_XOUT_H)
Wire.endTransmission(false);
Wire.requestFrom(ADXL345, 6, true); // Read 6 registers total, each axis value is stored in 2 registers
X_out = ( Wire.read()| Wire.read() << 8); // X-axis value
X_out = X_out/256; //For a range of +-2g, we need to divide the raw values by 256, according to the datasheet
Y_out = ( Wire.read()| Wire.read() << 8); // Y-axis value
Y_out = Y_out/256;
Z_out = ( Wire.read()| Wire.read() << 8); // Z-axis value
Z_out = Z_out/256;
Serial.print("Xa= ");
Serial.print(X_out);
Serial.print(" Ya= ");
Serial.print(Y_out);
Serial.print(" Za= ");
Serial.println(Z_out);
}
Description: So first we need to include the Wire.h library which is used for the I2C communication. If you want to learn more on how the I2C communication works and how to use it with Arduino you can check my other detailed tutorial for it.
Each device that uses the I2C communication has a unique I2C address, and this address can be found in the datasheet of the sensor (ADXL345 Datasheet). So, once we define the address and the variables for the three outputs, in the setup section, first, we need to initialize the wire library and then set the accelerometer in measuring mode. In order to do that, if we take a look at the datasheet again, we can see that we need to set the bit D3 of the POWER_CTL register HIGH.
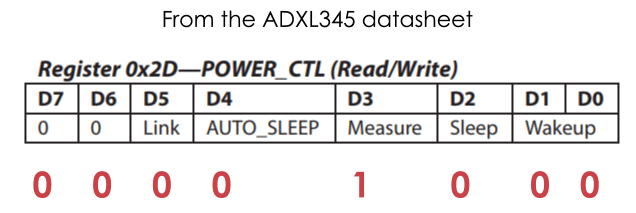
So, using the beginTransmission() function we start the communication, then using the write() function we tell which register we want to access, and again using the write() function we set the D3 bit HIGH, by writing the number 8 in decimal which correspond to setting the bit D3 HIGH.
// Set ADXL345 in measuring mode Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345); // Start communicating with the device Wire.write(0x2D); // Access/ talk to POWER_CTL Register - 0x2D // Enable measurement Wire.write(8); // (8dec -> 0000 1000 binary) Bit D3 High for measuring enable Wire.endTransmission();
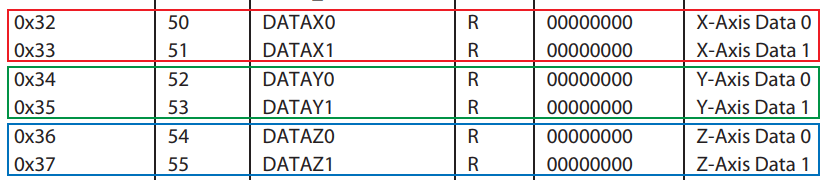
In the loop section now we read the data from the sensor. The data for each axis is stored in two bytes or registers. We can see the addresses of these registers from the datasheet.
In order to read them all, we start with the first register, and the using the requestionFrom() function we ask to read the 6 registers. Then using the read() function, we read the data from each register, and because the outputs are twos complements we combine them appropriately to get the correct values.
// === Read acceleromter data === // Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345); Wire.write(0x32); // Start with register 0x32 (ACCEL_XOUT_H) Wire.endTransmission(false); Wire.requestFrom(ADXL345, 6, true); // Read 6 registers total, each axis value is stored in 2 registers X_out = ( Wire.read()| Wire.read() << 8); // X-axis value X_out = X_out/256; //For a range of +-2g, we need to divide the raw values by 256, according to the datasheet Y_out = ( Wire.read()| Wire.read() << 8); // Y-axis value Y_out = Y_out/256; Z_out = ( Wire.read()| Wire.read() << 8); // Z-axis value Z_out = Z_out/256;
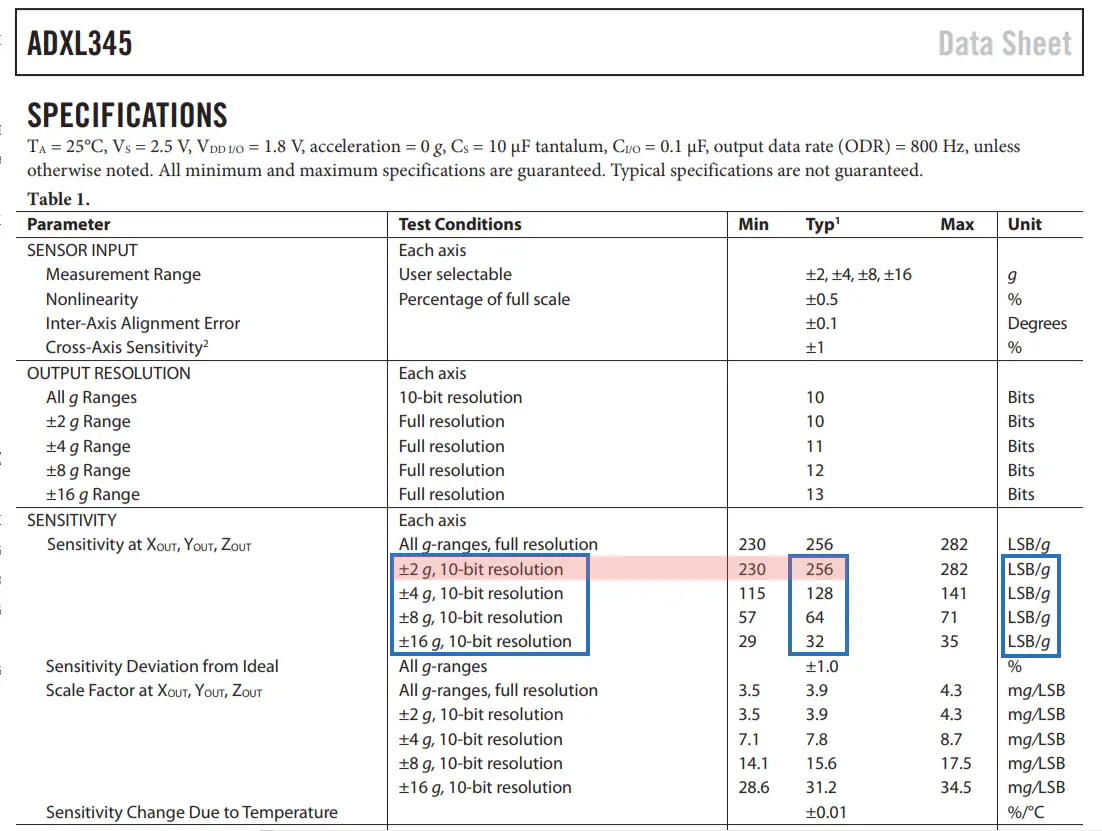
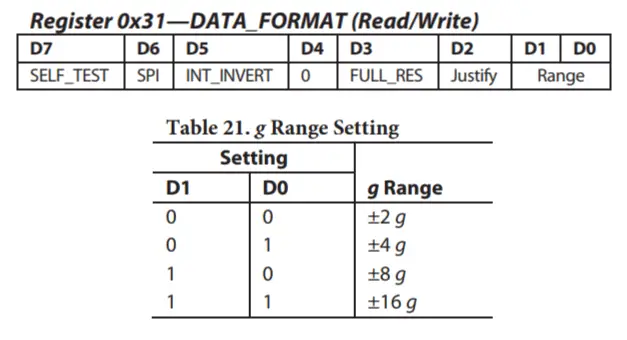
The output values from the sensor actually depend on the selected sensitivity, which can vary from +- 2g to +-16g. The default sensitivity is +-2g so that’s why we need to divide the output by 256 in order to get values from -1 to +1g. The 256 LSB/g means that we have 256 counts per g.
Depending on the application we can select the appropriate sensitivity. In this case, for tracking orientation, +-2g sensitivity is fine, but for application where we need to sense higher acceleration force from like sudden movements, shocks and so on, we can choose some of the other sensitivity ranges using the DATA_FORMAT register and its D1 and D0 bits.
ADXL345 Acceleromter Calibration
Nevertheless, once we read the data, we can simply print it on the serial monitor to check whether the values are as expected. In my case, the values I was getting were not exactly as they should be, especially the Z-axis which had a noticeable error of 0.1g.
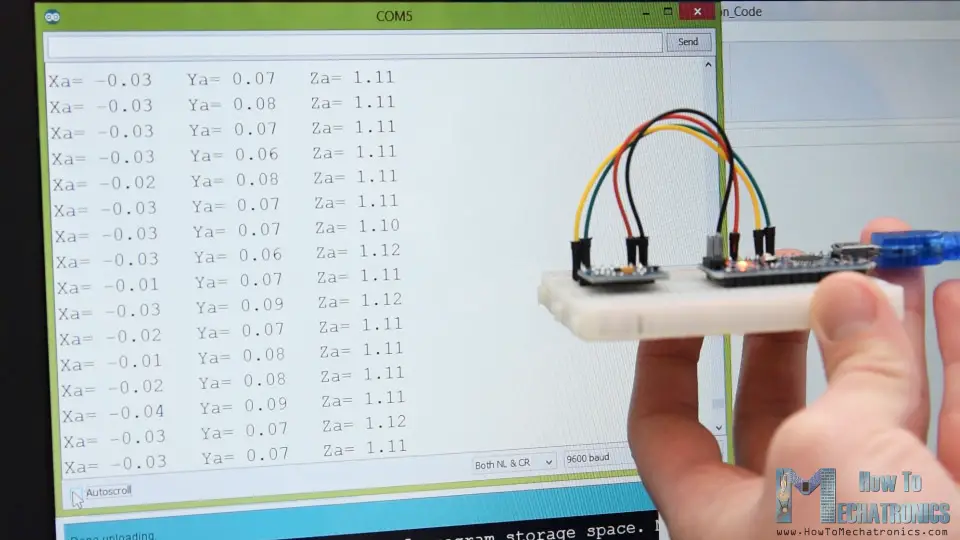
To solve this issue, we need to calibrate the accelerometer using the 3 offset calibration registers, and here’s how we can do that. So, we need to position the sensor flat, and print the RAW values without dividing them by 256.
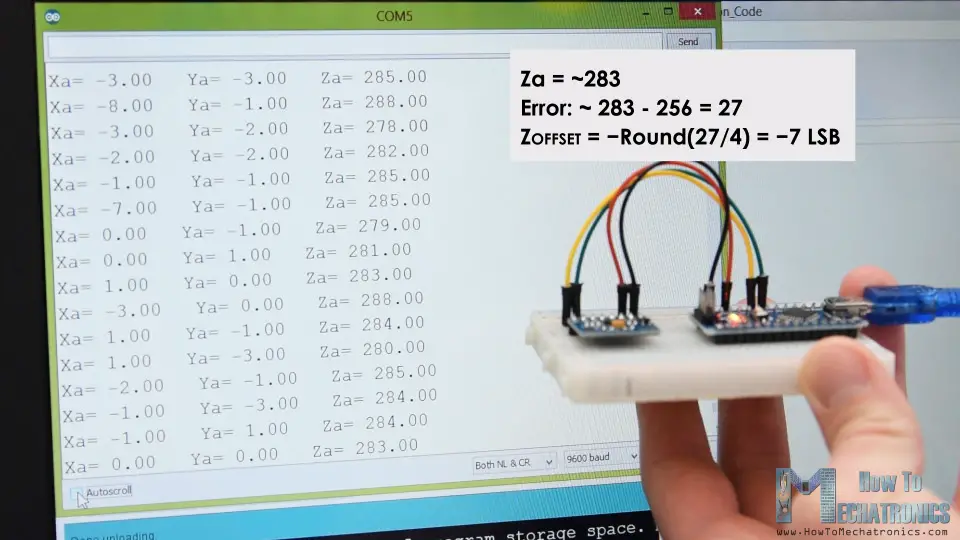
From here now we can notice the how much the outputs are off, in my case, the Z output was around 283. That’s difference of 27 in positive. Now we need to divide this value by 4, and that will give use the number that we need to write to the Z-axis offset register. If we upload the code now, the Z-axis output will be exactly 256, or 1g as it should be.
// This code goes in the SETUP section // Off-set Calibration //X-axis Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345); Wire.write(0x1E); // X-axis offset register Wire.write(1); Wire.endTransmission(); delay(10); //Y-axis Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345); Wire.write(0x1F); // Y-axis offset register Wire.write(-2); Wire.endTransmission(); delay(10); //Z-axis Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345); Wire.write(0x20); // Z-axis offset register Wire.write(-7); Wire.endTransmission(); delay(10);
If needed we should calibrate the other axis using the same method. And just a quick note that this calibration is not permanently written to the registers. We need to do write these values to the registers at each power up of the sensor.
Once we are done with the calibration, we can now finally calculate the Roll and Pitch, or the rotation around the X-axis and the rotation around the Y axis in degrees, using these two formulas.
// Calculate Roll and Pitch (rotation around X-axis, rotation around Y-axis) roll = atan(Y_out / sqrt(pow(X_out, 2) + pow(Z_out, 2))) * 180 / PI; pitch = atan(-1 * X_out / sqrt(pow(Y_out, 2) + pow(Z_out, 2))) * 180 / PI;
For more details how these formulas work, you can check this Freescale Semiconductor application note.
Arduino and ADXL345 Accelerometer Orientation Tracking – 3D Visualization
Ok, let’s make the accelerometer 3D visualization example now.
![]()
So, we are using the same code, which sends the Roll and Pitch values through the serial port. Here’s the complete Arduino code:
/*
Arduino and ADXL345 Accelerometer - 3D Visualization Example
by Dejan, https://howtomechatronics.com
*/
#include <Wire.h> // Wire library - used for I2C communication
int ADXL345 = 0x53; // The ADXL345 sensor I2C address
float X_out, Y_out, Z_out; // Outputs
float roll,pitch,rollF,pitchF=0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initiate serial communication for printing the results on the Serial monitor
Wire.begin(); // Initiate the Wire library
// Set ADXL345 in measuring mode
Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345); // Start communicating with the device
Wire.write(0x2D); // Access/ talk to POWER_CTL Register - 0x2D
// Enable measurement
Wire.write(8); // Bit D3 High for measuring enable (8dec -> 0000 1000 binary)
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(10);
//Off-set Calibration
//X-axis
Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345);
Wire.write(0x1E);
Wire.write(1);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(10);
//Y-axis
Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345);
Wire.write(0x1F);
Wire.write(-2);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(10);
//Z-axis
Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345);
Wire.write(0x20);
Wire.write(-9);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(10);
}
void loop() {
// === Read acceleromter data === //
Wire.beginTransmission(ADXL345);
Wire.write(0x32); // Start with register 0x32 (ACCEL_XOUT_H)
Wire.endTransmission(false);
Wire.requestFrom(ADXL345, 6, true); // Read 6 registers total, each axis value is stored in 2 registers
X_out = ( Wire.read() | Wire.read() << 8); // X-axis value
X_out = X_out / 256; //For a range of +-2g, we need to divide the raw values by 256, according to the datasheet
Y_out = ( Wire.read() | Wire.read() << 8); // Y-axis value
Y_out = Y_out / 256;
Z_out = ( Wire.read() | Wire.read() << 8); // Z-axis value
Z_out = Z_out / 256;
// Calculate Roll and Pitch (rotation around X-axis, rotation around Y-axis)
roll = atan(Y_out / sqrt(pow(X_out, 2) + pow(Z_out, 2))) * 180 / PI;
pitch = atan(-1 * X_out / sqrt(pow(Y_out, 2) + pow(Z_out, 2))) * 180 / PI;
// Low-pass filter
rollF = 0.94 * rollF + 0.06 * roll;
pitchF = 0.94 * pitchF + 0.06 * pitch;
Serial.print(rollF);
Serial.print("/");
Serial.println(pitchF);
}
Now in the Processing development environment we need to receive these values and use them to rotate the 3D object that we will create. Here’s the complete Processing code:
/*
Arduino and ADXL345 Accelerometer - 3D Visualization Example
by Dejan, https://howtomechatronics.com
*/
import processing.serial.*;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.io.IOException;
Serial myPort;
String data="";
float roll, pitch;
void setup() {
size (960, 640, P3D);
myPort = new Serial(this, "COM8", 9600); // starts the serial communication
myPort.bufferUntil('\n');
}
void draw() {
translate(width/2, height/2, 0);
background(33);
textSize(22);
text("Roll: " + int(roll) + " Pitch: " + int(pitch), -100, 265);
// Rotate the object
rotateX(radians(roll));
rotateZ(radians(-pitch));
// 3D 0bject
textSize(30);
fill(0, 76, 153);
box (386, 40, 200); // Draw box
textSize(25);
fill(255, 255, 255);
text("www.HowToMechatronics.com", -183, 10, 101);
//delay(10);
//println("ypr:\t" + angleX + "\t" + angleY); // Print the values to check whether we are getting proper values
}
// Read data from the Serial Port
void serialEvent (Serial myPort) {
// reads the data from the Serial Port up to the character '.' and puts it into the String variable "data".
data = myPort.readStringUntil('\n');
// if you got any bytes other than the linefeed:
if (data != null) {
data = trim(data);
// split the string at "/"
String items[] = split(data, '/');
if (items.length > 1) {
//--- Roll,Pitch in degrees
roll = float(items[0]);
pitch = float(items[1]);
}
}
}
Description: So here, we need to include the serial library, define the serial port and the baud rate which needs to match we the baud rate of the uploaded Arduino sketch. Then we read the incoming data and put it into the appropriate roll and pitch variables. In the main draw loop, we use these values to rotate the 3D object, and in this case that’s a simple box with has a particular color and a text on it.
If we run the sketch, the 3D object will appear and it will track the orientation of the accelerometer sensor. We can notice here that the object is actually a bit shaky and that’s because the accelerometer captures not just the gravitational force, but also small forces generated by the movements of our hand. In order to get smoother result, we can use a simple Low-pass filter. Here I implemented such a filter in the Arduino code, which it takes 94% of the previous state and adds 6% of the current state or angle.
// Low-pass filter rollF = 0.94 * rollF + 0.06 * roll; pitchF = 0.94 * pitchF + 0.06 * pitch;
With this filter, we can notice that the object moves a lot smoother now, but there is also a side effect and that’s slower responsiveness. We can also notice that we are missing the Yaw, or rotation around the Z-axis. Using only the 3-axis accelerometer data we are not able to calculate the Yaw.
In order to do that and improve the overall performance of our orientation tracking sensor, we actually need to include an additional sensor, a gyroscope, and fuse its data with the accelerometer.
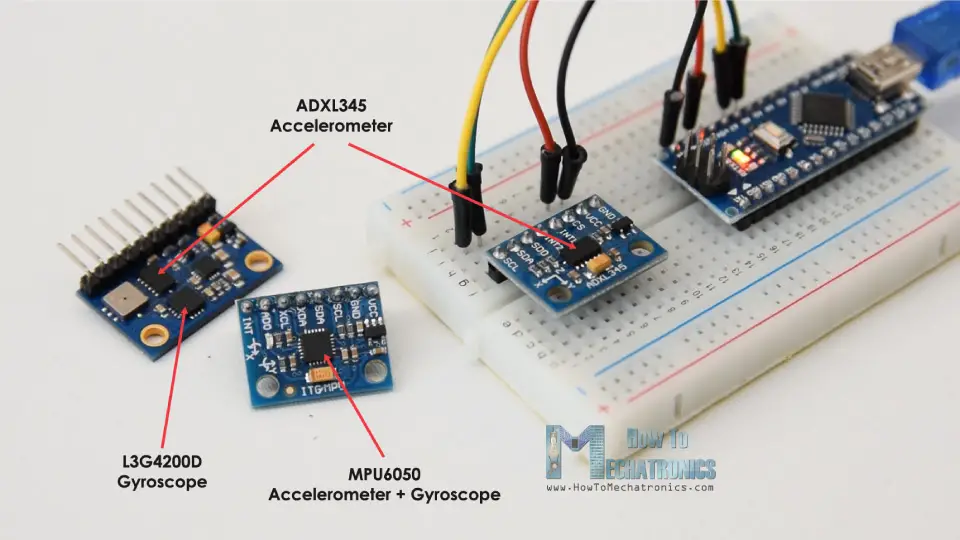
So, we can either use the ADXL345 accelerometer in combination some gyroscope sensor, or use the MPU6050 IMU which has both 3-Axis accelerometer and 3-Axis gyroscope integrated on a single chip. You can find more detailed tutorial on this sensor in my next video.
I hope you enjoyed this tutorial and learned something new. Feel free to ask any question in the comments section below and don’t forget to check my collection of Arduino Projects.
The post How To Track Orientation with Arduino and ADXL345 Accelerometer appeared first on HowToMechatronics.
from HowToMechatronics https://ift.tt/2FztT6f
“Faster, Smaller, Quieter”: Analog Devices Shows Off Silent Switcher 2 Buck Regulator at APEC
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2HIUzDY
How Telecom Is Transforming Rural India
This report shares an overview of the potential of the telecom industry in rural India and the various technologies that can help drive the initiatives. India has no dearth of technological and business innovations for rural areas. However, telecom policies and scams have created a negative impact on the growth of this sector in rural […]
The post How Telecom Is Transforming Rural India appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2UTuEMX
TDA11105PS/N3/3 COLOR TV CHROMA IC DATA SHEET AND PINOUT PDF
1 IFVO
2 VP2
3 VCC AUDIO
4 PLLIF
5GND2
6 DECSDEM
7 FMDEMOUT
8 EHTO
9 AGC
10 IREF
11CSC
12IF IN2
13 IF IN 1
14 VDRA
15 VDRB
16 AVLEW
17 DECBG
18 SECPLL
19 GNG1
20 PHL1FL
21 PHL2FL
22 VP1
23 DECDIG
24 XTALOUT
25 XTALIN
26 IR
27 MUTE
28 TILT
29 KEY
30 BAND2
31 BAND1
32 TUNNING
33 VDDP
34 SCL
35 SDA
36
37 TV/AV
38 STANDBY
39
40 VDD
41GND5
42 VPE
43 VDDA
44 BOUT
45 GOUT
46 ROUT
47 BLKIN
48 BCLIN
49 PB
50 YS/CVBS
51 PR/C3
52 YOUT
53 YSYNC
54 VP3
55 GND 3
56 HOUT
57 FBISO
58 LSR
59 LSL
60 C2/C3/C4
61 AIN3/IN1R
62 CVBSE/Y2
63 A/N2/N1L
64 CVBS4/Y4
TDA9370PS/N2/AI1399 COLOR TV CHROMA IC DATA SHEET AND PINOUT PDF
 |
| TDA9370PS-N2-AI1399 |
TDA9370PS pin voltage tda9370ps/n3/a/1717 pin voltage tda9370ps/n3/a/1930 pin voltage tda9370ps n3 a 1717 pin detail tda9370ps/n3/a/1930 circuit diagram tda9370ps/n3/a/1747 tda9370ps/n3/a/1717 onida tda9370ps/n3/a/1710 datasheet tda9370ps/n3/a/1747 pin details
TDA9381PS/N2/3/0489 COLOR TV CHROMA IC DATA SHEET AND PINOUT PDF
The UOC ultimate one chip TDA9381PS/N2/3/0489 is adopted in this chassis. This IC is the first available component that contains the complete control and small signal functionality needed for a TV application in one device.
TDA9381PS/N3/3/1959 COLOR TV CHROMA IC DATA SHEET AND PINOUT
The UOC ultimate one chip TDA9381PS/N3/3/1959 is adopted in this chassis. This IC is the first available component that contains the complete control and small signal functionality needed for a TV application in one device.
How To Make Your Own Laptop Power Bank?
 In this video, the presenter will show you how to create a Laptop PowerBank. It mainly consists of a Li-Ion battery pack and one buck and a boost converter. This way the PowerBank can get charged up through the Laptop power supply and afterwards charge up the Laptop directly to give it an additional run […]
In this video, the presenter will show you how to create a Laptop PowerBank. It mainly consists of a Li-Ion battery pack and one buck and a boost converter. This way the PowerBank can get charged up through the Laptop power supply and afterwards charge up the Laptop directly to give it an additional run […]
The post How To Make Your Own Laptop Power Bank? appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2HSExqb
Saturday 23 March 2019
RISC-V Foundation Hosting Worldwide Series of Getting Started with RISC-V Events
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2HONi4P
Friday 22 March 2019
New LED Drivers from Taiwan Semiconductor Reach Many Automotive Applications
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2FuHqMs
Unlock The Door To Future With Smart Fabric
 The introduction of conductive threads and wearable electronics together with the introduction of Lilypad Arduino microcontroller and Google’s Project Jacquard has revived the interest in the everyday article of clothing as a computing and interaction platform. How about all that while not the necessity for onboard electronics or batteries? The UW computer researchers have created […]
The introduction of conductive threads and wearable electronics together with the introduction of Lilypad Arduino microcontroller and Google’s Project Jacquard has revived the interest in the everyday article of clothing as a computing and interaction platform. How about all that while not the necessity for onboard electronics or batteries? The UW computer researchers have created […]
The post Unlock The Door To Future With Smart Fabric appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2JykqjR
Simple Obstacle-Avoiding Robot
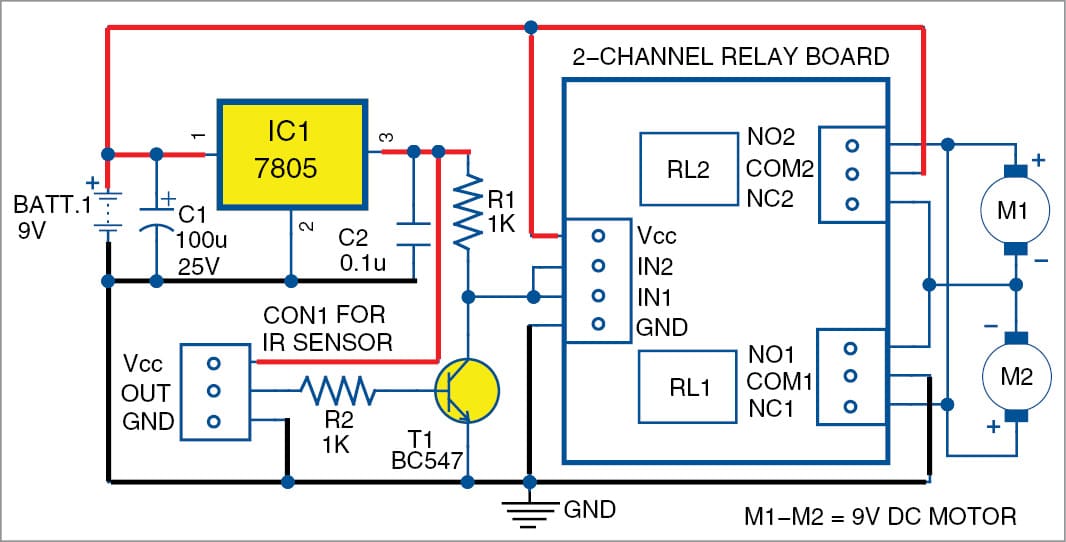 Presented here is an obstacle-avoidance robot without microcontroller (MCU). The obstacle-avoidance feature is commonly found in autonomous cars and robots. Most obstacle-avoidance robots are costly and difficult to build because of MCUs. This project is simple and does not use any complex circuitry except a relay driver. The author’s prototype is shown in Fig. 1. […]
Presented here is an obstacle-avoidance robot without microcontroller (MCU). The obstacle-avoidance feature is commonly found in autonomous cars and robots. Most obstacle-avoidance robots are costly and difficult to build because of MCUs. This project is simple and does not use any complex circuitry except a relay driver. The author’s prototype is shown in Fig. 1. […]
The post Simple Obstacle-Avoiding Robot appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2WfNlue
Thursday 21 March 2019
New Osilloscopes from Keysight Aim For Maker and Education Markets
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2Okq2wH
TDA 9370 COLOUR TV CHROMA IC DATASHEET AND PINOUT
TDA 9370PS/N2/AI1148 DATA SHEET AND PINOUT
TDA9370PS pin voltage tda9370ps/n3/a/1717 pin voltage tda9370ps/n3/a/1930 pin voltage tda9370ps n3 a 1717 pin detail tda9370ps/n3/a/1930 circuit diagram tda9370ps/n3/a/1747 tda9370ps/n3/a/1717 onida tda9370ps/n3/a/1710 datasheet tda9370ps/n3/a/1747 pin details
TDA9570H/N3/A/1783 COLOUR TV CHROMA IC DATASHEET AND PINOUT
Wednesday 20 March 2019
Applications And Advantages Of Using Li-Fi For Data Transfer
 Li-Fi, which uses visible light for communication, is 100 times faster than Wi-Fi, which uses radio frequencies. Visible light communication (VLC) is a data communication method that uses visible light between 400THz and 800THz (Tera-Hertz) frequency; wavelength is 780nm to 375nm. It is a subset of optical wireless communication technologies. VLC technology uses fluorescent lamps […]
Li-Fi, which uses visible light for communication, is 100 times faster than Wi-Fi, which uses radio frequencies. Visible light communication (VLC) is a data communication method that uses visible light between 400THz and 800THz (Tera-Hertz) frequency; wavelength is 780nm to 375nm. It is a subset of optical wireless communication technologies. VLC technology uses fluorescent lamps […]
The post Applications And Advantages Of Using Li-Fi For Data Transfer appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2HQIT1p
Silanna Touts Efficiency and Ease of Design with World’s First Active Clamp Flyback Controller
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2JpiV7m
New I/O Expander from Diodes Incorporated Offers Low-Voltage Compatibility
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2ThgHGV
TDA 12155PS N3 3 AT1 COLOUR TV CHROMA IC DATA SHEET
1 IFVO
2 VP2
3 VCC AUDIO
4 PLLIF
5GND2
6 DECSDEM
7 FMDEMOUT
8 EHTO
9 AGC
10 IREF
11CSC
12IF IN2
13 IF IN 1
14 VDRA
15 VDRB
16 AVLEW
17 DECBG
18 SECPLL
19 GNG1
20 PHL1FL
21 PHL2FL
22 VP1
23 DECDIG
24 XTALOUT
25 XTALIN
26 IR
27 MUTE
28 TILT
29 KEY
30 BAND2
31 BAND1
32 TUNNING
33 VDDP
34 SCL
35 SDA
36
37 TV/AV
38 STANDBY
39
40 VDD
41GND5
42 VPE
43 VDDA
44 BOUT
45 GOUT
46 ROUT
47 BLKIN
48 BCLIN
49 PB
50 YS/CVBS
51 PR/C3
52 YOUT
53 YSYNC
54 VP3
55 GND 3
56 HOUT
57 FBISO
58 LSR
59 LSL
60 C2/C3/C4
61 AIN3/IN1R
62 CVBSE/Y2
63 A/N2/N1L
64 CVBS4/Y4
Other ic datas are available in this link
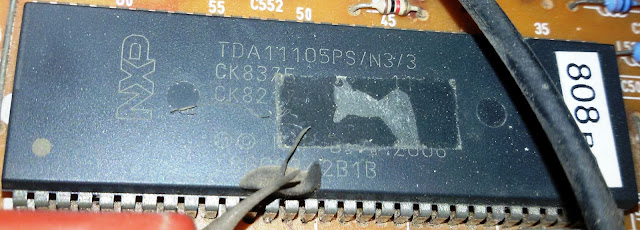
TDA 11105PS / V3/3/AO4 COLOUR TV CHROMA IC DATA SHEET
TDA 11105PS /N3/3/
1 IFVO
2 VP2
3 VCC AUDIO
4 PLLIF
5GND2
6 DECSDEM
7 FMDEMOUT
8 EHTO
9 AGC
10 IREF
11CSC
12IF IN2
13 IF IN 1
14 VDRA
15 VDRB
16 AVLEW
17 DECBG
18 SECPLL
19 GNG1
20 PHL1FL
21 PHL2FL
22 VP1
23 DECDIG
24 XTALOUT
25 XTALIN
26 IR
27 MUTE
28 TILT
29 KEY
30 BAND2
31 BAND1
32 TUNNING
33 VDDP
34 SCL
35 SDA
36
37 TV/AV
38 STANDBY
39
40 VDD
41GND5
42 VPE
43 VDDA
44 BOUT
45 GOUT
46 ROUT
47 BLKIN
48 BCLIN
49 PB
50 YS/CVBS
51 PR/C3
52 YOUT
53 YSYNC
54 VP3
55 GND 3
56 HOUT
57 FBISO
58 LSR
59 LSL
60 C2/C3/C4
61 AIN3/IN1R
62 CVBSE/Y2
63 A/N2/N1L
64 CVBS4/Y4
Tuesday 19 March 2019
Portable Health Checker Device with Blood Oxygen Monitor Project
Download Project Document/Synopsis With rapid medical development of our modern societies, the health care systems are becoming much more mature and professional. In order to reduce the current burden of public health system and promote the popularity of routine health self-check, this technique has been developed for making faster and accurate pre diagnoses with ease-of-use. […]
The post Portable Health Checker Device with Blood Oxygen Monitor Project appeared first on NevonProjects.
from NevonProjects https://ift.tt/2OfxFEt
Advanced Car & Scooty Training Driving School Management System
Download Project Document/Synopsis This Advanced Motor Driving School Management system can reduce the efforts of human power and wealth very much, and ensure driving-training school’s information resource to be utilized effectively. The motor driving trainers has to handle several students at a time. This will provide drawback in terms of communicating with students for his […]
The post Advanced Car & Scooty Training Driving School Management System appeared first on NevonProjects.
from NevonProjects https://ift.tt/2Oh1IMo
Monday 18 March 2019
Advanced Employee Management System Project Using PHP
Download Project Document/Synopsis Human resources describe the people who work for a company or organization and the department is responsible for managing resources related to employees. A human resource is a single person or employee within your organization. Human resources refer to all of the people you employ. The manual method is used to maintain […]
The post Advanced Employee Management System Project Using PHP appeared first on NevonProjects.
from NevonProjects https://ift.tt/2W9oJTT
Mobility: Electronic Toll, Standing Tall
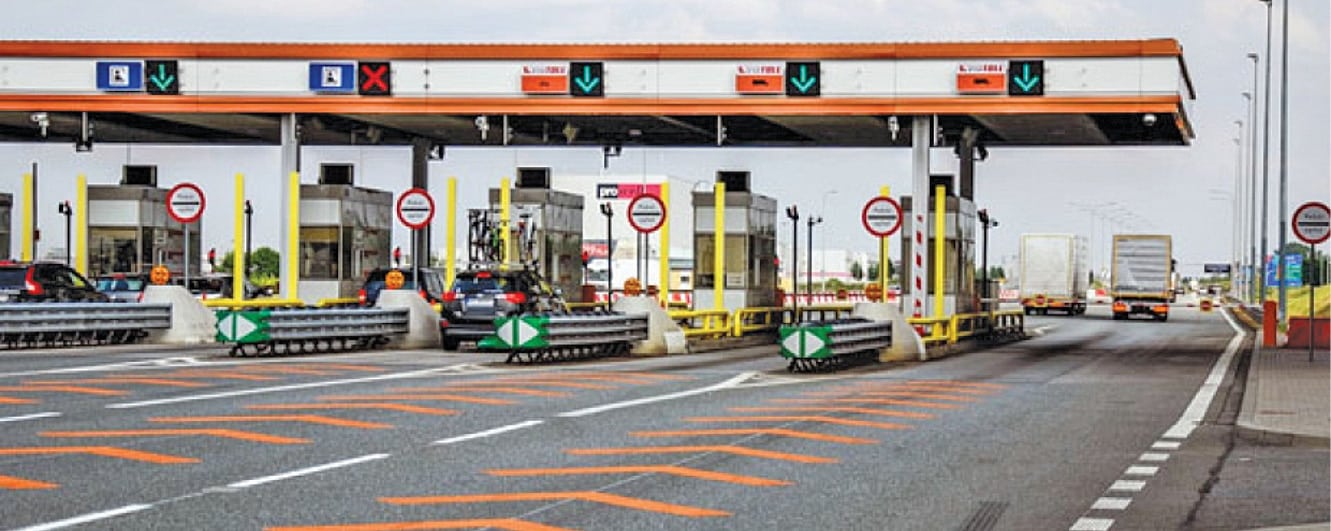 Electronic toll collection technology was developed to eliminate delays on toll roads by collecting tolls electronically. Recently, frequent traffic jams at Sirhaul Toll Plaza on Delhi-Gurugram expressway forced the district administration to close the 12-lane plaza permanently. People commuting from New Delhi to Gurugram and back recall the difficulty faced in passing through this toll […]
Electronic toll collection technology was developed to eliminate delays on toll roads by collecting tolls electronically. Recently, frequent traffic jams at Sirhaul Toll Plaza on Delhi-Gurugram expressway forced the district administration to close the 12-lane plaza permanently. People commuting from New Delhi to Gurugram and back recall the difficulty faced in passing through this toll […]
The post Mobility: Electronic Toll, Standing Tall appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2TIV7jH
Understanding DNL and INL Specifications of a DAC
from All About Circuits Technical Articles https://ift.tt/2TPPq3D
APEC 2019 Focuses on the Needs of the Practical, Practicing Power Engineer
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2Tfxr1g
How To Use Modern Multi-Processor Application Programs
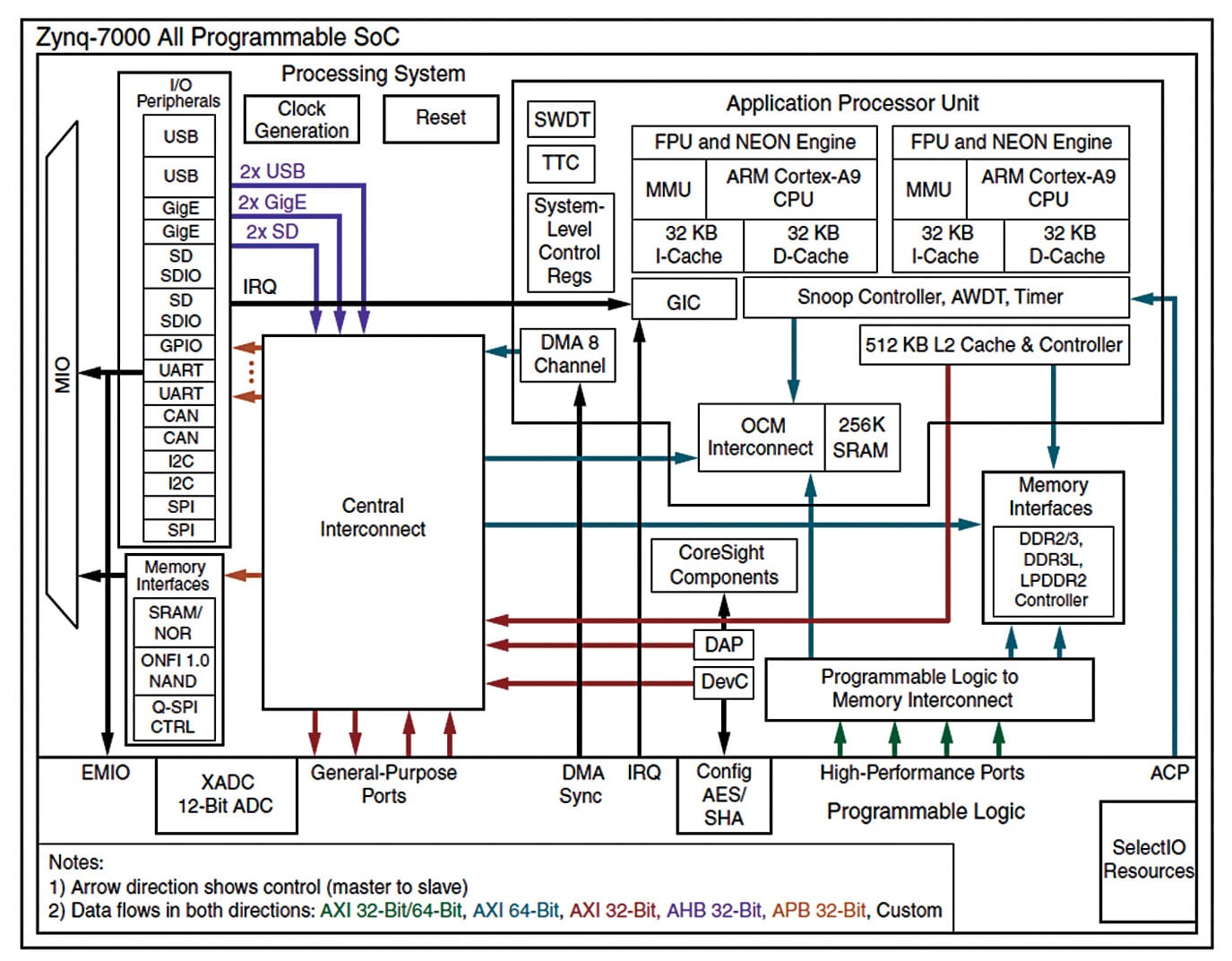 An application built with the hybrid model of parallel programming can run on a computer cluster using both OpenMP and message passing interface. Modern embedded applications are becoming complex and demanding with respect to code reuse, as platforms and applications are being developed and implemented rapidly. Implementation is a combination of hardware and software, and […]
An application built with the hybrid model of parallel programming can run on a computer cluster using both OpenMP and message passing interface. Modern embedded applications are becoming complex and demanding with respect to code reuse, as platforms and applications are being developed and implemented rapidly. Implementation is a combination of hardware and software, and […]
The post How To Use Modern Multi-Processor Application Programs appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2HsMR0O
Saturday 16 March 2019
Can Near Field Communication Be Secure In the IoT? NXP’s New NFC Tag Aims For Highest Security
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2TEOZcg
Cobots And Augmented Reality Changing The World
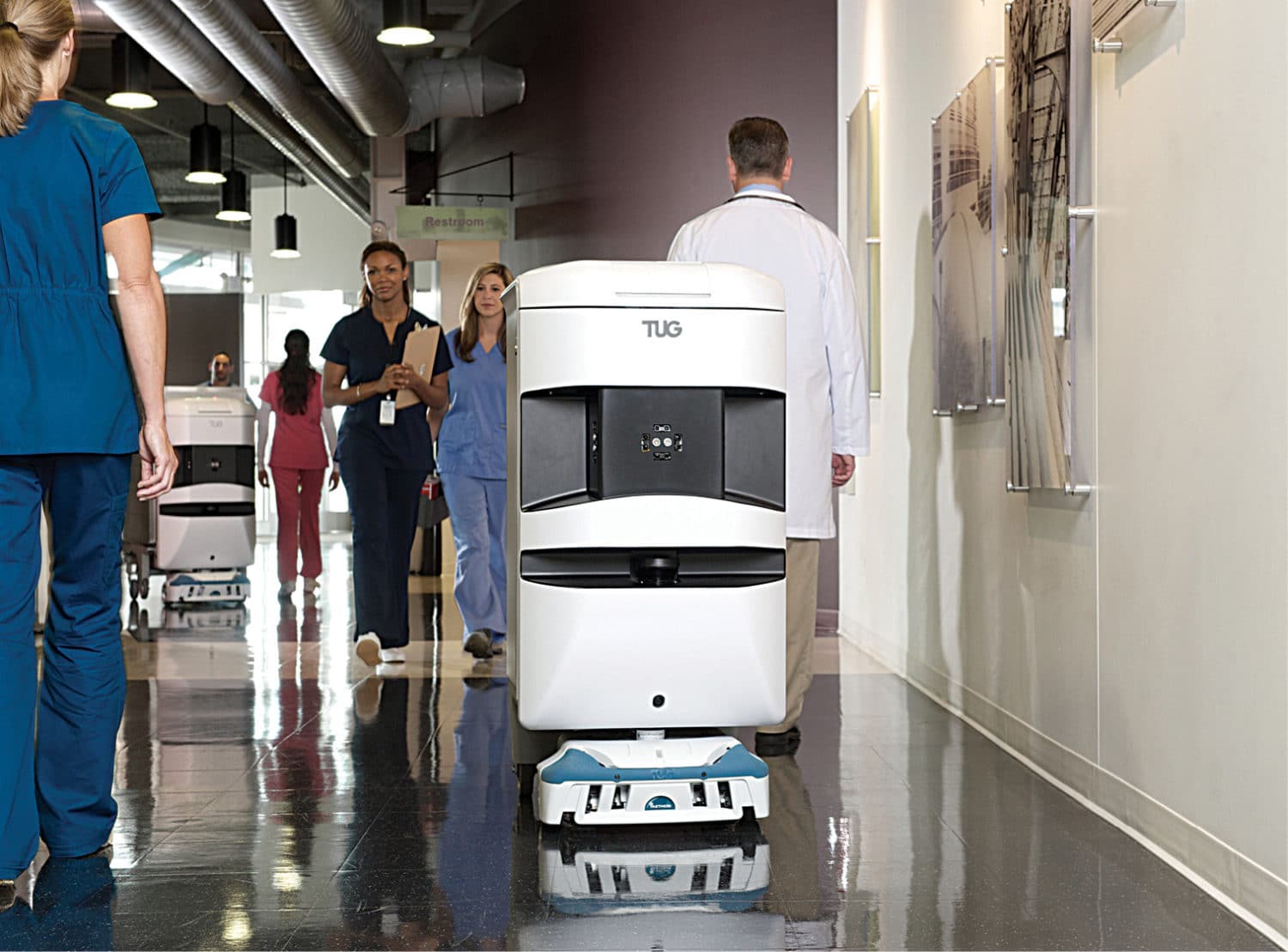 In this article, we discuss cobots and AR from the perspective of motivation, technology and business, while adding a social spin to these. Cobots (or collaborative robots) and augmented reality (AR) are advancing societal development. Cobots are finding use in sectors like manufacturing and medical for detecting errors and increasing productivity and, hence, motivating entrepreneurs […]
In this article, we discuss cobots and AR from the perspective of motivation, technology and business, while adding a social spin to these. Cobots (or collaborative robots) and augmented reality (AR) are advancing societal development. Cobots are finding use in sectors like manufacturing and medical for detecting errors and increasing productivity and, hence, motivating entrepreneurs […]
The post Cobots And Augmented Reality Changing The World appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2u7jKHA
Friday 15 March 2019
Ensuring Safety While Filling Air Inside A Tyre
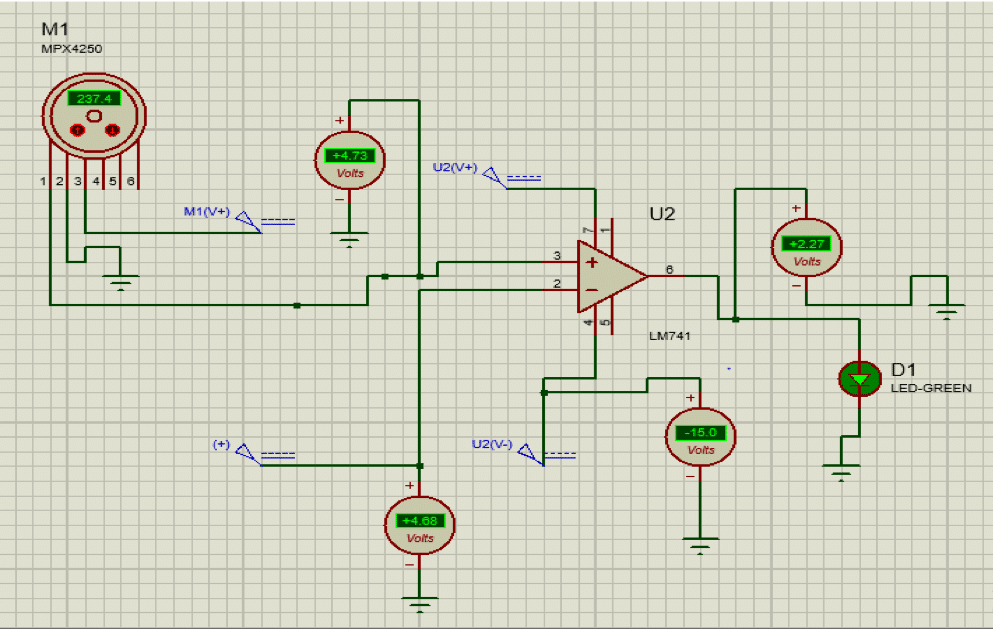 In this article, our focus is related to air pressure while filling air in the tyre. This is important because the tyre may get burst and create many other problems due to excessive air pressure inside. So, we have proposed one method in which, one can detect the pressure of air in the tyre while […]
In this article, our focus is related to air pressure while filling air in the tyre. This is important because the tyre may get burst and create many other problems due to excessive air pressure inside. So, we have proposed one method in which, one can detect the pressure of air in the tyre while […]
The post Ensuring Safety While Filling Air Inside A Tyre appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2UFX5hc
Different Types of Semiconductor Devices
In this article, we will see a little bit about Semiconductor Devices in general, what are some commonly known Types of Semiconductor Devices and many other aspects of Semiconductors.
Introduction
Over the last 70 years, semiconductors became a crucial element in the manufacturing of electronics. Since the invention of the Transistor, the world of electronics has always been on an exponential curve in terms of research, development, manufacturing, bringing up new devices and technologies.
Electronic Devices are all about handling information i.e. high-speed transmission, acquisition and processing in fields of industries and manufacturing, communications, arts, medicine and even in warfare.
But all these can be dialed back to the heart of modern electronics and its manufacturing: Semiconductor Devices.
Even though an electronic system is manufactured with the help of metals, insulators and semiconductors (more about these later), the semiconductors are considered the backbone of electronics.
What is a Semiconductor?
Before going in to the discussion about different types of Semiconductor Device, it is essential to have an idea about what a semiconductor is.
Simply speaking Semiconductors are materials that are neither conductors nor insulators. Expanding a little bit more on this, materials are classified into Conductors, Insulators and Semiconductors based on their ability of conduct electricity.
Conductors are materials with very good electricity carrying capacity. Usually metals have good electrical conductivity and you can find Copper or Aluminium in your home’s electrical wiring.
On the contrary, Insulators are materials with very bad electrical conductivity. Glass, wood and paper are good examples of Insulators.
Now let us talk about the important category of material for our discussion i.e. the semiconductors. At room temperature, Semiconductors are materials with lower electrical conductivity than Conductors but with higher electrical conductivity than Insulators.
NOTE: For more detailed understanding about semiconductors, you have to dig deep into the beautifully complicated Quantum Mechanics, which is “certainly” out of scope of this discussion.
Semiconductor Materials
Speaking in terms of electrical conductivity with units of Ω-1 cm-1, semiconductor materials are those with electrical conductivity between 10-9 Ω-1 cm-1 and 102 Ω-1 cm-1.
Traditionally, group IV elements like Silicon (Si) and Germanium (Ge) are considered the Elemental Semiconductor Materials i.e. semiconductors with only single atom species.
There are other types of semiconductor materials which can be formed by combining elements from group III with that of elements of group V and they are known as Compound Semiconductors. Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) is the best-known semiconductor material in this category and in fact it the second to Silicon as the most commonly used semiconductor material.
What are Semiconductor Devices?
In simple words, Semiconductor devices are a type of electronic components that designed, developed and manufactured based on the Semiconductor materials like Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge) and Gallium Arsenide (GaAs).
Since their use in late 1940’s (or early 1950’s), semiconductors became the main material in the manufacturing of electronics and its variants like optoelectronics and thermoelectronics.
Before the usage of semiconductor materials in electronic devices, vacuum tubes were used design of electronic components. The main difference between vacuum tubes and semiconductor devices is that in vacuum tubes, the conduction of electrons occurs in gaseous state while in case of semiconductor device, it happens in “solid state”.
Semiconductor devices can be found as both discrete components devices as well as integrated circuits.
Why Semiconductors?
The main reason for using Semiconductor Devices (and hence the underlying Semiconductor Materials) in the manufacturing of electronics devices and components is the ability to easily manipulate its conductivity of charge carriers i.e. electrons and holes.
As mentioned earlier, the electrical conductivity of semiconductor materials lies between that of conductors and insulators. Even this conductivity can be further controlled by external or internal factors like electric field, magnetic field, light, temperature and mechanical distortion.
Ignoring the external factors like temperature and light for now, a process called Doping is generally performed to the semiconductor materials, where an impurity is introduced into its structure to change the structural as well as electrical properties.
A pure semiconductor is known as Intrinsic Semiconductor while an impure or doped semiconductor is known as Extrinsic Semiconductor.
When the number of free electrons in the semiconductor structure is increased after doping, the semiconductor is known as n-type semiconductor. Similarly, if the holes are increased, it is known as p-type semiconductor.
Different Types of Semiconductor Devices
The following is a small list of some of the commonly used semiconductor devices. Based on the physical structure of the device, the following list is categorized into Two-terminal Devices and Three-terminal Devices.
Two-terminal Semiconductor Devices
- Diode
- Schottky Diode
- Light Emitting Diode (LED)
- DIAC
- Zener Diode
- Photo Diode (Photo Transistor)
- PIN Diode
- Laser Diode
- Tunnel Diode
- Photo Cell
- Solar Cell
- Gunn Diode
- IMPATT Diode
- TVS Diode (Transient Voltage Suppression Diode)
- VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser)
Three-terminal Semiconductor Devices
- Bipolar Transistor
- Field Effect Transistor
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
- Darlington Transistor
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)
- TRIAC
- Thyristor
- Unijunction Transistor
There are also a few four-terminal semiconductors like Optocoupler (Photocoupler) and Hall-effect Sensor.
For more information on some of the above mentioned semiconductor devices, read “P-N Junction Diode“, “Transistor“, “Thyristor“.
Applications of Semiconductor Devices
As mentioned earlier, semiconductor devices are the basis of almost all electronic devices. Some of the applications of semiconductor devices are:
- Transistors are the main components in various integrated circuits like Microprocessors.
- In fact, they are the main components in the construction of logic gates and other digital circuits.
- Transistors are also used in analog circuits like amplifiers and oscillators.
The post Different Types of Semiconductor Devices appeared first on Electronics Hub.
from Electronics Hub https://ift.tt/2W0G1mb
New Dual Simultaneous Sampling ADCs from ADI Feature On-Chip Oversampling Blocks
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2Y01v4v
Basics Of Smith Chart
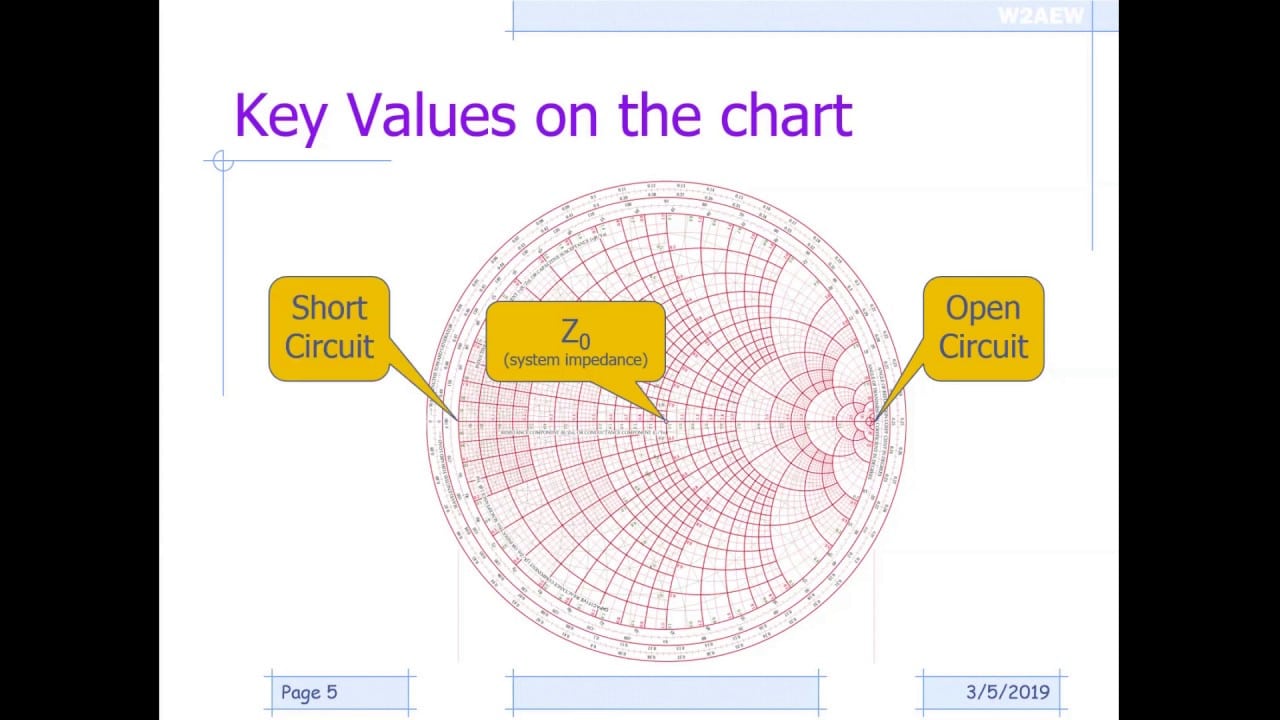 In this video, the presenter will cover the basics of the Smith Chart – what it is, how you plot complex impedance, obtain VSWR, return loss, reflection coefficient, transmission line effects and compute impedance matching networks. Courtesy: w2aew
In this video, the presenter will cover the basics of the Smith Chart – what it is, how you plot complex impedance, obtain VSWR, return loss, reflection coefficient, transmission line effects and compute impedance matching networks. Courtesy: w2aew
The post Basics Of Smith Chart appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2TSjSsT
Thursday 14 March 2019
Time-To-Digital Converters Emerge as Key Components in Autonomous Vehicles
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2O8Pwx6
New STMicro BLDC Controller Takes a Highly Integrated Approach to Motor Control
from All About Circuits News https://ift.tt/2Hz20wO
Image Processing Using MATLAB: Basic Operations (Part 1 of 4)
 In this series of four articles, fundamentals, as well as advanced topics of image processing using MATLAB, are discussed. The articles cover basic to advanced functions of MATLAB’s image processing toolbox (IPT) and their effects on different images. Part I in this series gives a brief introduction to digital images and MATLAB followed by basic […]
In this series of four articles, fundamentals, as well as advanced topics of image processing using MATLAB, are discussed. The articles cover basic to advanced functions of MATLAB’s image processing toolbox (IPT) and their effects on different images. Part I in this series gives a brief introduction to digital images and MATLAB followed by basic […]
The post Image Processing Using MATLAB: Basic Operations (Part 1 of 4) appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2HiUdDN
A Novel Architecture For Decimal Conversion In 8-Bit MCU
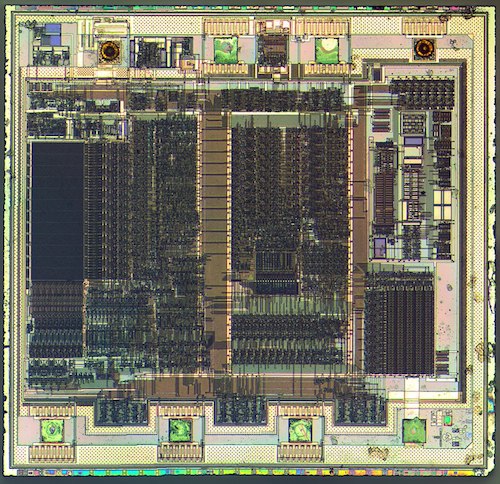 This article highlights common errors in 8-bit instruction sets, and introduces a novel architecture for decimal conversion instructions, especially in 8051, 8086, 8085 and PIC microcontrollers (MCUs). Statistical analysis of different methodologies has revealed that decimal conversion instructions in microprocessors and MCUs do not offer an error-free process. Bugs can be common for the above-mentioned […]
This article highlights common errors in 8-bit instruction sets, and introduces a novel architecture for decimal conversion instructions, especially in 8051, 8086, 8085 and PIC microcontrollers (MCUs). Statistical analysis of different methodologies has revealed that decimal conversion instructions in microprocessors and MCUs do not offer an error-free process. Bugs can be common for the above-mentioned […]
The post A Novel Architecture For Decimal Conversion In 8-Bit MCU appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2Faxfg3
When Working With Emerging Technologies – Sanity Is The Key!
 Once upon a time… Once upon a time (read as several years ago), while I was working with a home appliance manufacturing company in my early days of career, an interesting incident happened. We used to report to a Senior Manager back then, and he was quite steadfast in pushing certain things, especially when he […]
Once upon a time… Once upon a time (read as several years ago), while I was working with a home appliance manufacturing company in my early days of career, an interesting incident happened. We used to report to a Senior Manager back then, and he was quite steadfast in pushing certain things, especially when he […]
The post When Working With Emerging Technologies – Sanity Is The Key! appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2F3qWcE
Online Railway Concession Form for College System
Download Project Document/Synopsis Local train is the lifeline of people, and students are no exceptions. Education without train travelling is a rarely seen case. Students below the age of 25 are given a facility by Central and Western Railway, Mumbai, giving them concession in train pass if they use the local train services for going […]
The post Online Railway Concession Form for College System appeared first on NevonProjects.
from NevonProjects https://ift.tt/2UAkL6D
Wednesday 13 March 2019
How To Manage Thousands of Devices In A Secure, Scalable Way
 Providing comprehensive, in-depth security protection for Internet of Things (IoT) applications in today’s connected world brings challenges on multiple levels. The Renesas Synergy Platform provides a unique set of hardware and software security capabilities that combine to meet the requirements of securing IoT devices and networks, including the ability to ensure secure, scalable manufacturing and […]
Providing comprehensive, in-depth security protection for Internet of Things (IoT) applications in today’s connected world brings challenges on multiple levels. The Renesas Synergy Platform provides a unique set of hardware and software security capabilities that combine to meet the requirements of securing IoT devices and networks, including the ability to ensure secure, scalable manufacturing and […]
The post How To Manage Thousands of Devices In A Secure, Scalable Way appeared first on Electronics For You.
from Electronics For You https://ift.tt/2JckhSZ