Introduction
Smart Cards used as credit/debit cards have evolved over the years and revolutionized the banking industry since the late 1980’s and have now found widespread applications in other areas like security systems, transport systems, retail, healthcare and most recently in IoT technology.
Different types of smart cards are available for different applications. The essential differences in smart card types are mainly because of the different electronic components that are part of the smart card system which includes both the card and the card reader. This article explores how smart cards evolved over the years, the different types of Smart Cards, and details of how they work and where they are used.
Need for Smart Cards
Smart cards evolved from magnetic stripe cards which were not really smart and did not have any inbuilt intelligence. Magnetic stripe cards store data by modifying the magnetism (polarity) of tiny iron-based magnetic particles which are contained in the plastic-like film on the card.
This is the same principle as tape-cassettes which store audio/music. In case of the cards, the card number, name, CVC, expiration date and service code are stored on the tape. When the card is swiped on the reader, the data contained on the tape is read to verify the information on the card.
As this static data on the tape can be easily replicated or copied, there was a need for more intelligent and dynamic cards with increased security. This paved the way for smart cards.
Different Types of Smart Cards
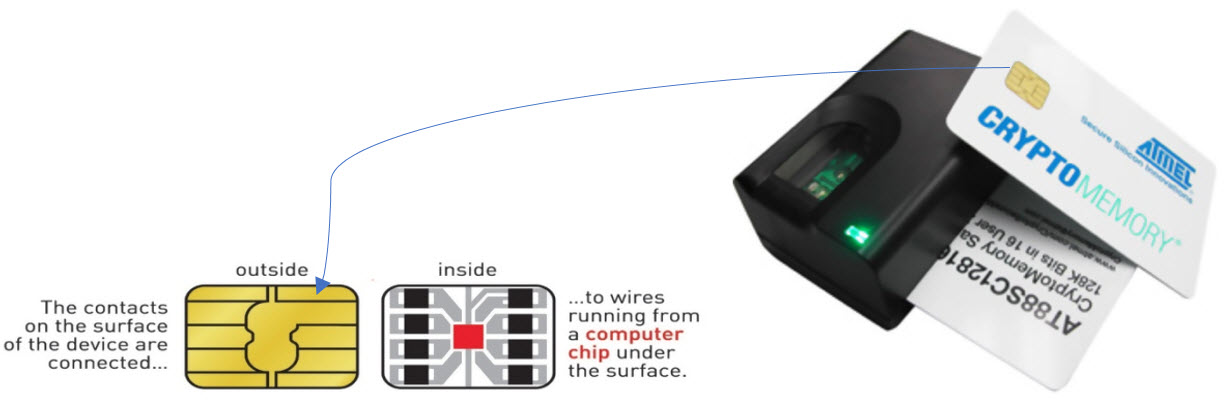
A Smart Card contains an embedded integrated circuit which makes it possible for it to store data and/or house a programmable microcontroller. The electrical specifications of the smart card, are based on the ISO 7816 specification which also governs the dimensions and location of the different contacts points in the smart card.
Following are the two main categories of smart cards currently available and the technology at work in each case.
- Contact Type
- Contact-less Type
Contact Type
Contact is required between the card and the card reader in this case.
Contact-less Type
The card and card reader need not touch in this case, however the card should be held near to the reader.
How do Smart Cards Work?
We will now describe in details how each type of Smart Card works
Contact Smart Cards
This is basically a plastic card which can be read only when it is brought into contact with the card reader. It derives its power from the card reader. It typically has a contact area of approximately 1 cm2 with several gold plated contact pads. The contact pads provide electrical connectivity to the reader. Communication protocols for contact smart cards are as defined in ISO 7816-3 specifications.
Contactless Smart Cards
As the name suggests, contactless smart cards can be read without bringing the card in contact with the reader. The card communicates with the reader through RFID induction technology which also powers the card. The RFID technology used in this case works over a short range (less than 4 inches).
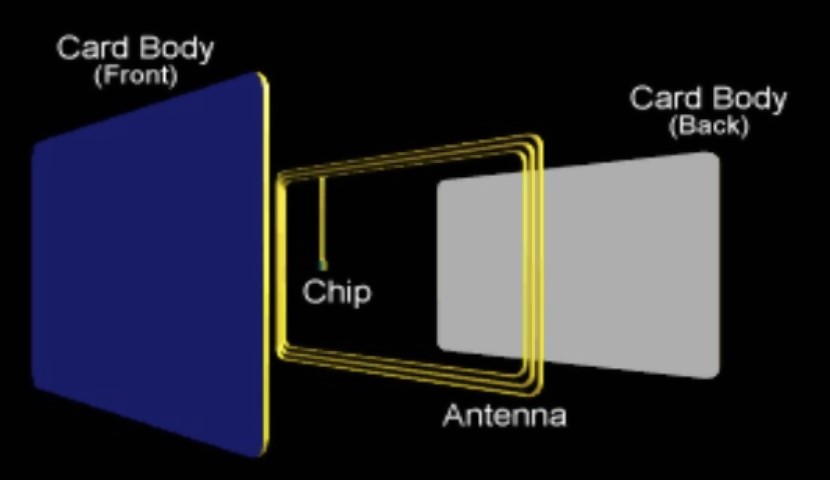
As such, the card should be held near to the reader. The card includes an embedded secure microcontroller or equivalent intelligence, internal memory and a small antenna for communicating with the reader.
When the card is brought into the electromagnetic field of the reader, the chip in the card is powered on. Once the chip is powered on, a wireless communication protocol is initiated and established between the card and the reader for data transfer.
Following image from secure tech alliance illustrates the contents of a contactless smart card. ISO/IEC 14443 defines the communication standards for contactless cards.
Applications
Contact smart cards come in two varieties. Memory cards which are primarily used only to store data and microprocessor cards which can also process information. Applications for these cards can be commonly seen in membership cards, loyalty cards, vending cards etc.
Contact less type of smart cards are commonly used in applications which require protection of personal information and fast, secure transactions. Examples include, identity cards, fare payment cards, credit/debit cards etc.
Looking at the future
- Both contact and contactless smart cards have found multiple applications in various industries.
- Technologically, the introduction of Near Field Communications (NFC) in mobile phones have enabled the use of mobiles wallets with smart card readers.
- Security of Smart Card systems is also being enhanced by integrating them with biometric fingerprint sensor technology.
- This will help to get rid of pin based authentication or signatures which are required for high value transactions at present.
The post Electronics of Smart Cards appeared first on Electronics Hub.
from Electronics Hub http://bit.ly/31PbhZ1
No comments:
Post a Comment