If Statement (Conditional Statement)
The if() statement is the most basic of all programming control structures. It allows you to make something happen or not, depending on whether a given condition is true or not. It looks like this:if (someCondition) {
// do stuff if the condition is true
}
There is a common variation called if-else that looks like this:
if (someCondition) {
// do stuff if the condition is true
} else {
// do stuff if the condition is false
}
There's also the else-if, where you can check a second condition if the first is false:
if (someCondition) {
// do stuff if the condition is true
} else if (anotherCondition) {
// do stuff only if the first condition is false
// and the second condition is true
}
You'll use if statements all the time. The example below turns on an
LED on pin 13 (the built-in LED on many Arduino boards) if the value
read on an analog input goes above a certain threshold.
Hardware Required
- Arduino or Genuino Board
- Potentiometer or variable resistor
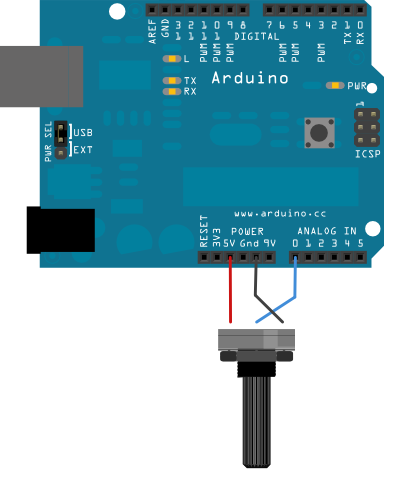
Circuit
click the image to enlarge
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
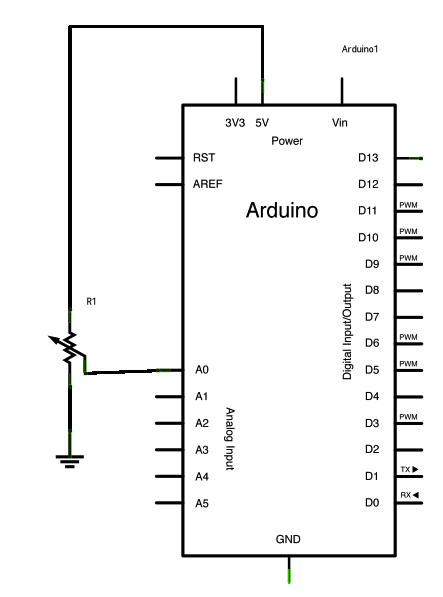
Schematic
click the image to enlargeCode
In the code below, a variable calledanalogValue is used
to store the data collected from a potentiometer connected to the board
on analogPin 0. This data is then compared to a threshold value. If the
analog value is found to be above the set threshold the built-in LED
connected to digital pin 13 is turned on. If analogValue is found to be < (less than) threshold, the LED remains off.
/*
Conditionals - If statement
This example demonstrates the use of if() statements.
It reads the state of a potentiometer (an analog input) and turns on an LED
only if the potentiometer goes above a certain threshold level. It prints the
analog value regardless of the level.
The circuit:
- potentiometer
Center pin of the potentiometer goes to analog pin 0.
Side pins of the potentiometer go to +5V and ground.
- LED connected from digital pin 13 to ground
- Note: On most Arduino boards, there is already an LED on the board connected
to pin 13, so you don't need any extra components for this example.
created 17 Jan 2009
modified 9 Apr 2012
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/IfStatement
*/
// These constants won't change:
const int analogPin = A0; // pin that the sensor is attached to
const int ledPin = 13; // pin that the LED is attached to
const int threshold = 400; // an arbitrary threshold level that's in the range of the analog input
void setup() {
// initialize the LED pin as an output:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
// initialize serial communications:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// read the value of the potentiometer:
int analogValue = analogRead(analogPin);
// if the analog value is high enough, turn on the LED:
if (analogValue > threshold) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
// print the analog value:
Serial.println(analogValue);
delay(1); // delay in between reads for stability
}
Conditionals - If statement
This example demonstrates the use of if() statements.
It reads the state of a potentiometer (an analog input) and turns on an LED
only if the potentiometer goes above a certain threshold level. It prints the
analog value regardless of the level.
The circuit:
- potentiometer
Center pin of the potentiometer goes to analog pin 0.
Side pins of the potentiometer go to +5V and ground.
- LED connected from digital pin 13 to ground
- Note: On most Arduino boards, there is already an LED on the board connected
to pin 13, so you don't need any extra components for this example.
created 17 Jan 2009
modified 9 Apr 2012
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/IfStatement
*/
// These constants won't change:
const int analogPin = A0; // pin that the sensor is attached to
const int ledPin = 13; // pin that the LED is attached to
const int threshold = 400; // an arbitrary threshold level that's in the range of the analog input
void setup() {
// initialize the LED pin as an output:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
// initialize serial communications:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// read the value of the potentiometer:
int analogValue = analogRead(analogPin);
// if the analog value is high enough, turn on the LED:
if (analogValue > threshold) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
// print the analog value:
Serial.println(analogValue);
delay(1); // delay in between reads for stability
}
See Also
- if()
- if...else
- analogRead()
- digitalWrite()
- serial.begin()
- serial.print()
- Arrays - A variation on the For Loop example that demonstrates how to use an array.
- ForLoopIteration - Control multiple LEDs with a for loop.
- switchCase - How to choose between a discrete number of values.
- switchCase2 - A second switch-case example, showing how to take different actions based on the characters received in the serial port.
- WhileStatementConditional - How to use a while loop to calibrate a sensor while a button is being read.
No comments:
Post a Comment